Commands
To work with commands, the Units: Commands service should be activated in the billing plan or account properties.
A command is a request sent to a unit so that it performs a certain action, such as sending its coordinates to the server, updating the configuration, stopping the engine, etc. Commands are created on the Commands tab of the unit properties.
Methods of sending commands
To send commands to the unit, you should have the following access rights to it:
- Send commands;
- the access rights specified in the command properties.
For sending commands automatically by means of jobs and notifications, you should also have:
- the Use unit in jobs, notifications, routes, retranslators right to the unit;
- the Create, edit and delete jobs right to the resource in which the job is created;
- the Create, edit and delete notifications right to the resource in which the notification is created.
There are several methods of sending commands to units and their groups:
- manually from the Monitoring tab;
- automatically by means of the Send a command to units job carried out according to the specified schedule;
- automatically by means of a notification with the Send a command action;
- manually from the application for iOS and Android.
Particularities of sending commands
When sending commands, take into account the following particularities:
- To send a command to a unit group, this command should be created in the properties of each unit, and the same name and type should be specified for it.
- The Send route and Send waypoints commands allow only manual sending, because you should specify the route parameters every time you send the command, not when you create it.
- The Upload configuration and Upload firmware commands created without selecting a file can’t be sent by means of a job or notification.
- The Send message to driver command can be sent to units not only using the methods described above, but also from the Chat with drivers window which shows the replies to your messages.
Sending commands from the “Monitoring” tab
To send commands from the Monitoring tab, you should enable the Commands option in the customizer of monitoring options.
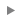
To send a command, follow the steps below.
- Click on the icon
 /
/  in the row or additional menu (
in the row or additional menu ( ) of a unit or group.
) of a unit or group.
- Select the required command from the list. It shows only those commands which you can send now, depending on the available transmission methods. If you are going to send a command to a unit group, the following icons can be displayed next to the commands:
 : you can send the command to all the units of the group;
: you can send the command to all the units of the group; : you can send the command only to some of the units (point to the icon to see the details).
: you can send the command only to some of the units (point to the icon to see the details).
- Click Next.
- If necessary, specify the additional parameters, for example, coordinates, the number of a digital input/output, the frequency of data sending, etc.
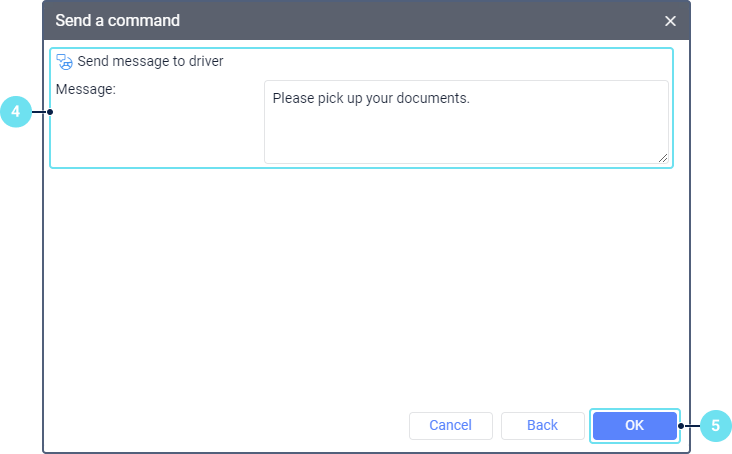
- Click OK.
The records of sending and executing the command are shown in the log.
After executing the Request configuration command, you can download the received file from the unit folder in the Disketta application. To find out the name of the required file, request data messages from the unit for the period within which the command was executed.
Information about the sent commands
You can get information about the sent commands from the following sources:
- Messages tab;
- Sent commands report;
- log (only for monitoring commands in real time).